1008. Construct Binary Search Tree from Preorder Traversal
Problem Statement
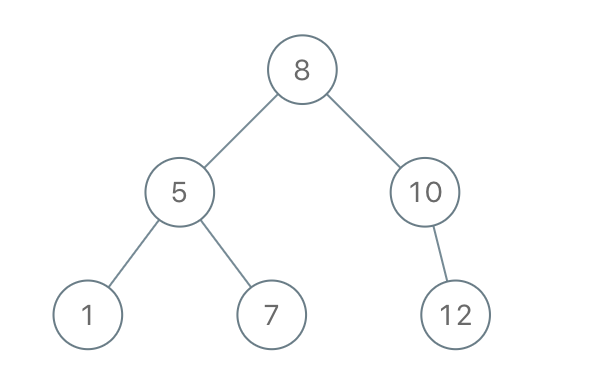
Input: preorder = [8,5,1,7,10,12]
Output: [8,5,10,1,7,null,12]Input: preorder = [1,3]
Output: [1,null,3]Intuition
Links
Video Links
Approach 1:
Approach 2:
Approach 3:
Approach 4:
Similar Problems
Last updated