1424. Diagonal Traverse II
Problem Statement
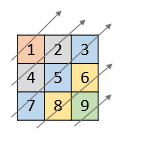
Input: nums = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
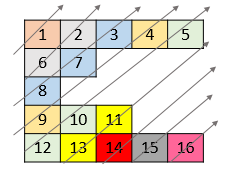
Output: [1,4,2,7,5,3,8,6,9]Input: nums = [[1,2,3,4,5],[6,7],[8],[9,10,11],[12,13,14,15,16]]
Output: [1,6,2,8,7,3,9,4,12,10,5,13,11,14,15,16]Intuition
Links
Video Links
Approach 1:
Approach 2:
Approach 3:
Approach 4:
Similar Problems
Last updated