654. Maximum Binary Tree
Problem Statement
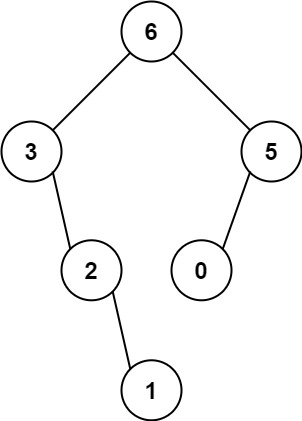
Input: nums = [3,2,1,6,0,5]
Output: [6,3,5,null,2,0,null,null,1]
Explanation: The recursive calls are as follow:
- The largest value in [3,2,1,6,0,5] is 6. Left prefix is [3,2,1] and right suffix is [0,5].
- The largest value in [3,2,1] is 3. Left prefix is [] and right suffix is [2,1].
- Empty array, so no child.
- The largest value in [2,1] is 2. Left prefix is [] and right suffix is [1].
- Empty array, so no child.
- Only one element, so child is a node with value 1.
- The largest value in [0,5] is 5. Left prefix is [0] and right suffix is [].
- Only one element, so child is a node with value 0.
- Empty array, so no child.Intuition
Links
Video Links
Approach 1:
Approach 2:
Approach 3:
Approach 4:
Similar Problems
Last updated