105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
Problem Statement
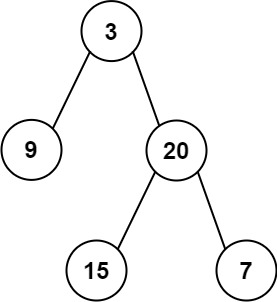
Input: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]Input: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1]
Output: [-1]Intuition
Links
Video Links
Approach 1:
Approach 2:
Approach 3:
Approach 4:
Similar Problems
Previous222. Count Complete Tree NodesNext106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
Last updated