863. All Nodes Distance K in Binary Tree
Problem Statement
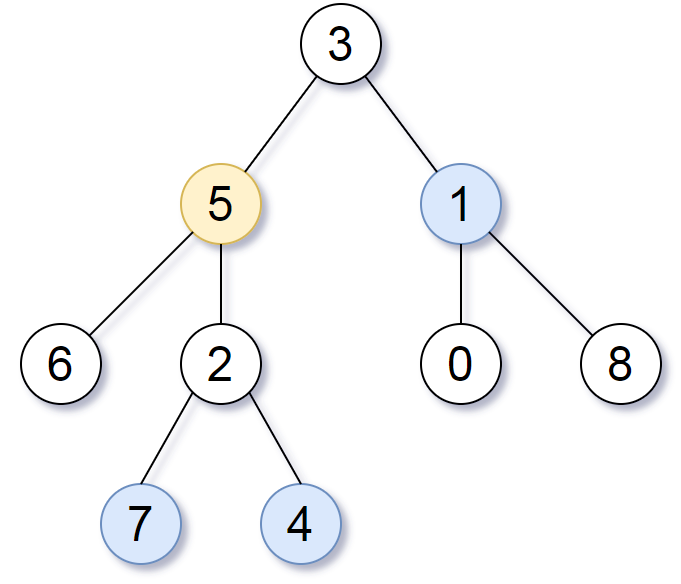
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, k = 2
Output: [7,4,1]
Explanation: The nodes that are a distance 2 from the target node (with value 5) have values 7, 4, and 1.Input: root = [1], target = 1, k = 3
Output: []Intuition
Links
Video Links
Approach 1:
Approach 2:
Approach 3:
Approach 4:
Similar Problems
Last updated