1547. Minimum Cost to Cut a Stick
Problem Statement
Input: n = 7, cuts = [1,3,4,5]
Output: 16
Explanation: Using cuts order = [1, 3, 4, 5] as in the input leads to the following scenario:
The first cut is done to a rod of length 7 so the cost is 7. The second cut is done to a rod of length 6 (i.e. the second part of the first cut), the third is done to a rod of length 4 and the last cut is to a rod of length 3. The total cost is 7 + 6 + 4 + 3 = 20.
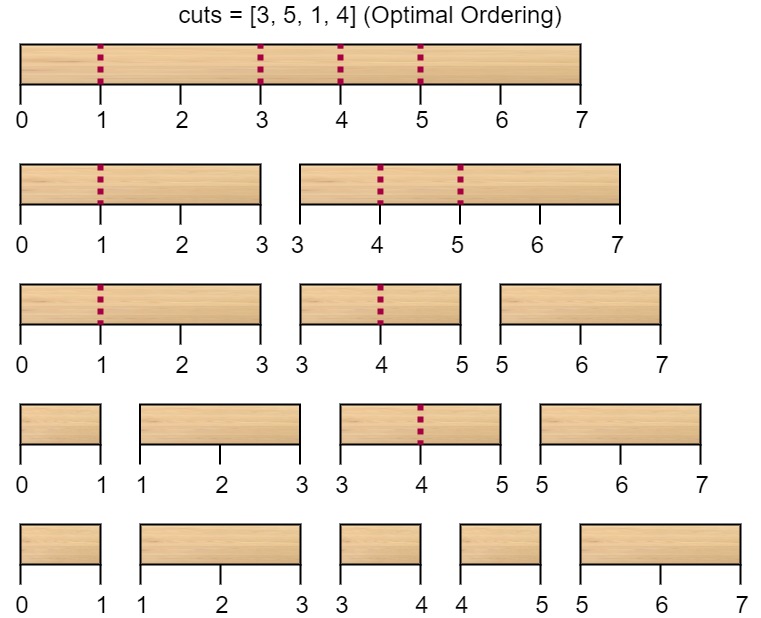
Rearranging the cuts to be [3, 5, 1, 4] for example will lead to a scenario with total cost = 16 (as shown in the example photo 7 + 4 + 3 + 2 = 16).Intuition
Links
Video Links
Approach 1:
Approach 2:
Approach 3:
Approach 4:
Similar Problems
Last updated