103. Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
Problem Statement
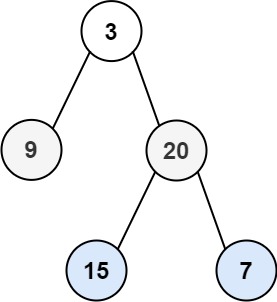
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[3],[20,9],[15,7]]Input: root = [1]
Output: [[1]]Input: root = []
Output: []Intuition
Links
Video Links
Approach 1:
Approach 2:
Approach 3:
Approach 4:
Similar Problems
Previous654. Maximum Binary TreeNext236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree / 235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
Last updated