450. Delete Node in a BST
Problem Statement
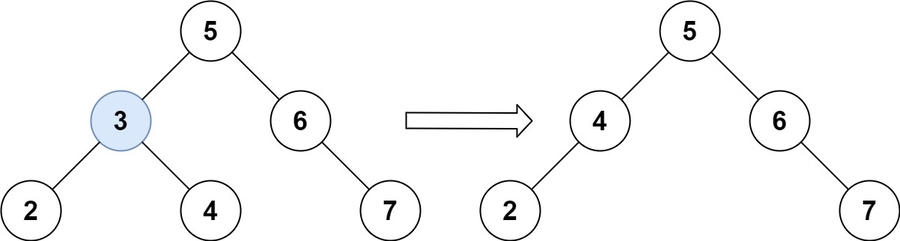
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 3
Output: [5,4,6,2,null,null,7]
Explanation: Given key to delete is 3. So we find the node with value 3 and delete it.
One valid answer is [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], shown in the above BST.
Please notice that another valid answer is [5,2,6,null,4,null,7] and it's also accepted.
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 0
Output: [5,3,6,2,4,null,7]
Explanation: The tree does not contain a node with value = 0.Intuition
Links
Video Links
Approach 1:
Approach 2:
Approach 3:
Approach 4:
Similar Problems
Last updated